Fabric-SDK-Node¶
This document explains about the fabric-sdk-node CI process. The below steps explain what CI follows or executes when a patchset is submits to the fabric-sdk-node repository.
Whenever a patchset is submitted to the fabric-sdk-node repository, Jenkins triggers the CI build process to test and validate the patchset. Fabric-sdk-node CI verify and merge jobs are configured to test the patchset in the below environment.
The Hyperledger Fabric (and associated) projects utilize various tools and workflows for continuous project development. The fabric-sdk-node is currently utilizing the following versions in the Master and Release-1.0 and Release-1.1 branches.
Master:
- go version: v1.9.2
- docker version: 17.12.0-ce
- npm version: 8.9.4
Release-1.0:
- go version: v1.9
- docker version: 17.12.0-ce
- npm version: 6.9.5
Release-1.1:
- go version: v1.9.2
- docker version: 17.12.0-ce
- npm version: 8.9.4
If you would like to know more details on the tool versions, you can refer from any fabric-sdk-node jobs listed here fabric-sdk-node. Select one of the jobs, Click on any build number in the bottom left and view the output for details.
Build Process¶
There are several Jenkins job types that are common across Hyperledger Fabric projects. In some cases, you may or may not see all of the common job types in every project. This depends on the specific needs of that Hyperledger Fabric project. The CI configuration is prepared in Jenkins Job Builder to create, update and modify the Jenkins Jobs.
As part of the CI process, we create JJB’s (Jenkins Job Builder) in YAML format to configure Jenkins jobs. JJB has a flexible template system, so creating many similar jobs with a common configuration is easy. More about Jenkins Job Builder is available on the JJB webpage.
The following explains what happens when we submit a patch to the fabric-sdk-node repository.
When a patchset is submitted to fabric-sdk-node repository, the Hyperledger Community CI server (Jenkins) triggers Verify and jobs on x86_64 ans s390x platforms using the patchset’s parent commit which may or may not be the latest commit on fabric-sdk-node.
The following verify jobs are triggered.
fabric-sdk-node6-verify-x86_64
fabric-sdk-node8-verify-x86_64
As part of the CI process on fabric-sdk-node repository, the following tests are executed on x86_64(x) and s390x(z) platforms, see the arch value at the end of the job name to know on which platform we run this job.
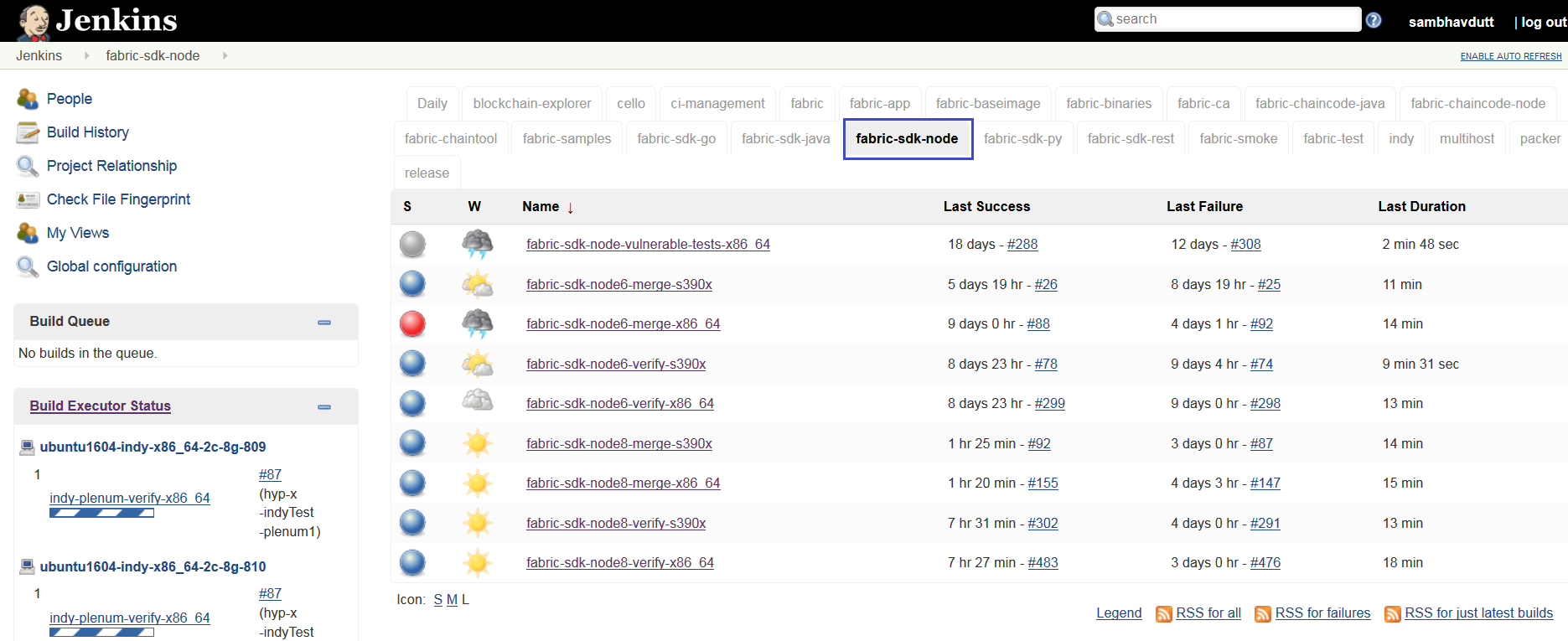
Views
Below is the process we execute in CI on fabric-sdk-node verify and merge jobs: Step 1: - Clone fabric & fabric-ca repositories:
- Clone the latest commit from the gerrit fabric repository and then check for the Branch Name, if the patch is triggered on fabric-sdk-node release-1.0 branch, we checkout to fabric release-1.0 branch.
- Build Docker Images:
- fabric-sdk-node makes use of just the peer and orderer images, we
build only peer-docker and order-docker docker images using
make peer-docker&make orderer-dockerto reduce the build time.
- fabric-sdk-node makes use of just the peer and orderer images, we
build only peer-docker and order-docker docker images using
The same proceess applies to fabric-ca repository too.
Step 2: - Once the images are ready, CI script execute docker-compose
file to spinup the network from /test/fixures directory.
docker-compose up >> dockerlogfile.log
Step 3: - After the network is up, install the nodejs version based on
the Job we are running. If the job name says
fabric-sdk-node8-verify-x86_64, script installs nodejs version
8.9.4 in x86_64 build machine
Step 4: - After the nodjs version installed, CI script executes
npm install , gulp & gulp ca commands to download all the
dependent packages.
Step 5: - Once the environment is ready, CI script executes
gulp test command which executes [‘clean-up’, ‘lint’, ‘pre-test’,
‘docker-ready’, ‘ca’] build tasks.
Above process is applicable to both ** verify ** and ** merge ** jobs.
After the builds are executed successfully, it sends a voting to gerrit patch set with a +1, or -1 if the build fails.
Next, on a successful code review(+1) and merge by the maintainers, Jenkins triggers the Merge jobs. The merge jobs for fabric-sdk-java perform all steps detailed above and also publish node modules to NPM Open Source Registry.
An initial validation is made to check the version of the npm modules created. The version of the created npm modules is compared with the version specified in package.json file. The package.json file holds the current npm details that include the version number too.
When the npm version matches with the current specified version in package.json file, this fabric client/fabric-ca client npm version is not published in Merge jobs.
If the npm module version does not match the current version in the package.json and it has a ‘snapshot’ in it’s version tag, it is published as the next unstable version of npm.
If the npm module matches the current existing npm version in the package.json file and it has a
snapshotin it’s version tag, it is incremented and published as the next unstable version for the existing npm version. For example, if the existing unstable npm version with thesnapshottag ends with number 84, the next unstable version is incremented by +1 and is stored with thesnapshottag ending with 85. The folowing are two unstable npm versions.fabric-client@1.1.0-snapshot.85 fabric-client@1.1.0-snapshot.84
The same process is followed in fabric-ca Merge jobs.If you wish to look at npm packages for fabric-client or fabric-ca-client, you can select the following links.
Once the tests are executed, Jenkins performs some pre-defined tasks to project the progress of each of the tests from beginning to end, also known as Post Build actions, In this case for the fabric-sdk-node.
- Jenkins publishes and displays the code coverage report on console output.
- The CI team configured one of Jenkins feature/plugin, the Cobertura code coverage report to publish the code coverage in a well presented format.
- Archive the build artifacts and display these build logs on the Jenkins console.
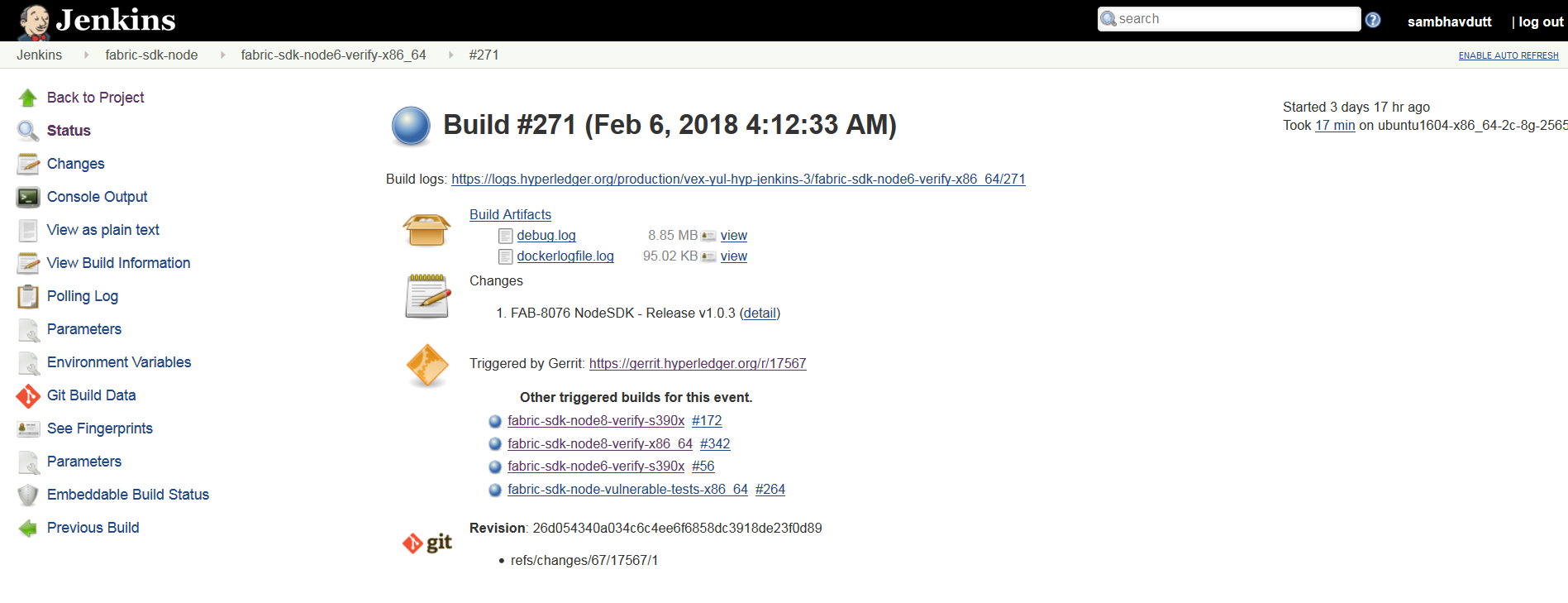
ConsoleOutPut
Build Notifications¶
The build results can be viewed on the Jenkins console, where depending on the result it displays with a colored bubble (green for success, red for failure) and a vote from the CI (+1 or -1) on the gerrit commit/change.
Trigger failed jobs through gerrit comments¶
Re-trigger of builds is possible in Jenkins by entering reverify in a comment to the gerrit change that retriggers all the verify jobs. To do so, follow the below process:
Step 1: Open the gerrit patchset for which you want to reverify the build
Step 2: Click on Reply, then type reverify and click Post
This kicks off all the fabric-sdk-node verify jobs. Once the build is triggered, verify the Jenkins console output and go through the log messages if you are interested in knowing how the build is making progress.
In somecases, Jenkins may fail only in one or two CI jobs due to which
network issues. In such cases, restarting all the fabric-sdk-node jobs
through reverify comment is not necessary. Instead, the developer
can post below comment to trigger the particular failed build:
reverify-node8z- to restart the build on sdk-node8-verify s390x platform.
reverify-node8x- to restart the build on sdk-node8-verify x86_64 platform.
reverify-node6z- to restart the build on sdk-node6-verify s390x platform.
reverify-node6x- to restart the build on sdk-node6-verify x86_64 platform.
Questions¶
Please reachout to us in #fabric-ci or #ci-pipeline RC channels for Questions or concerns related to fabric-sdk-node CI process.