Fabric¶
This document explains the CI process for the Fabric repository. The below steps explains what CI follows or executes when a patch set is submited to the Fabric repository.
Whenever a patchset is submitted to the Fabric repository, Jenkins triggers the CI build process to test and validate the patchset. Fabric CI verify and merge jobs are configured to test the patchset in the below environment.
The Hyperledger Fabric (and associated) projects utilize various tools and workflows for continuous project development. The Fabric CI is currently utilizing the following versions in the Master and Release-1.1, Release-1.0 branches.
Master:
- GO version:(e.g. v1.10) https://github.com/hyperledger/fabric/blob/master/ci.properties
- DOCKER version: 17.12.0-ce
- baseimage version:(e.g. 0.4.6) https://github.com/hyperledger/fabric/blob/196c0de7c1618952a8f342e406a1021203845eba/Makefile#L46
Release-1.0:
- GO version:(e.g. v1.7.5) https://github.com/hyperledger/fabric/blob/release-1.0/ci.properties
- DOCKER version: 17.12.0-ce
- baseimage version:(e.g. 0.4.6)
Release-1.1:
- GO version:(e.g. v1.9.2) https://github.com/hyperledger/fabric/blob/release-1.1/ci.properties
- DOCKER version: 17.12.0-ce
- baseimage version:(e.g. 0.4.6) https://github.com/hyperledger/fabric/blob/da14b6bae4a843dfb3fcece5a08ae0ea18488a7a/Makefile#L39
If you would like to know more details on the tool versions, you can refer from any of the Fabric jobs listed over here Fabric, select one of the jobs, Click on any build number in the bottom left and view the output for details.
There are several job types that are common across Hyperledger Fabric projects. In some cases, you may or may not see all of the common job types in every project. This depends on the specific needs of that Hyperledger Fabric project. The CI configuration is prepared in Jenkins Job Builder to create, update and modify the Jenkins Jobs.
As part of the CI process, we create JJBs (Jenkins Job Builder) in YAML format to configure Jenkins jobs. JJB has a flexible template system, so creating multiple jobs with a common configuration which is easy. More details about Jenkins Job Builder are available in the JJB webpage.
The following steps explains, what happens when a developer submits a patchset to the Fabric repository.
When a patchset is submitted to the Fabric repository, the Hyperledger Community CI server (Jenkins) triggers Verify jobs on x86_64 platform using the patchset’s parent commit which may or may not be the latest commit on Fabric.
Build Process¶
The Fabric verify build process is split up into multiple jobs. The initial job
(fabric-verify-build-checks-x86_64) is to build and publish docker images and binaries to
Nexus3 and Nexus2. These images are later pulled/downloaded in the downstream jobs, when the
triggered conditions meets in fabric-verify-build-checks-x86_64 CI job.
Below are the conditions to trigger relevant jobs based on the patchset:
fabric-verify-build-checks-x86_64job triggers when apatchsetis created and it validates the patchsets git commit message.If the commit message has a WIP, the above build job ignores to build the patchset and will not post a voting back to Fabric patchset. That means, this job skips the build process. You can see “WIP - No build” in the patchset’s result.
If the patchset has a non WIP in the commit message or if it is a documentation change with these file extensions (.rst, .md, .py, .png,.css,.html and .ini), the above job posts
Run DocBuildcomment and sends Fabric voting asF1-VerifyBuild=+1 F2-SmokeTest=+1 F3-UnitTest=+1against the patchset.* Run DocBuild - This comment triggers `fabric-docs-build-x86_64` CI job. Once the doc build is successfully executed, Jenkins sends Fabric vote as `F2-DocsBuild=+1` otherwise as `F2-DocsBuild=-1`If the patchset has non WIP in the commit message or a code and documentation changes (see the above file extensions), fabric-verify-build-checks-x86_64 executes the below flow. The below flow also applies to the code only patchset excluding documentation build process.
* Executes `make basic-checks`, `make docker` (builds, re-tag and publish images to nexus3), `make dist` (builds binaries) and publishes to nexus2. If any of these make targets fails, fabric-verify-build-checks-x86_64 sends `F1-VerifyBuild=-1` to the Fabric patchset otherwise it sends `F1-VerifyBuild=+1` and triggers **DocsBuild** and **SmokeTest** jobs parallely by posting below comments to the patchset. * Run DocsBuild - This comment triggers `fabric-docs-build-x86_64` job and posts `F2-DocsBuild=+1` if successful, otherwise `F2-DocsBuild=-1`. See the doc RTD output in the nexus log server. What happens in **fabric-docs-build-x86_64** job Step1: Builds the documentation changes: - Extracts the documentation files(.md, .rst, .txt, .py, .png, .css, .html & .ini) from the patchset submitted and builds the documentation after verification checks like syntax, and tox verification. This job is triggered only when a patchset contains documentation files. Step2: Documented output is published to Nexus: - Once the documentation build is successful, it is archived, and the archives built are published to Nexus. * Run SmokeTest - This comment triggers `fabric-smoke-tests-x86_64` job and posts `F2-SmokeTest=+1` to the patchset and triggers Unit-Test job by posting `Run UnitTest` comment if successful, otherwise posts `F2-SmokeTest=-1` which doesn't trigger Unit-Test job. * Run UnitTest - This comment triggers `fabric-verify-unit-tests-x86_64` job and posts `F3-UnitTest=+1` vote against the patchset if successful, otherwise `F3-UnitTest=-1`.
Conditions to merge the patch set¶
Maintainers have to look for +1 on all the labels before they merge the patchsets. The votes on the patchset should look like below.
F1-VerifyBuild +1 Hyperledger Jobbuilder
F2-DocBuild +1 Hyperledger Jobbuilder
F2-SmokeTest +1 Hyperledger Jobbuilder
F3-UnitTest +1 Hyperledger Jobbuilder
patchset is not elible to merge, if it even gets one -1.
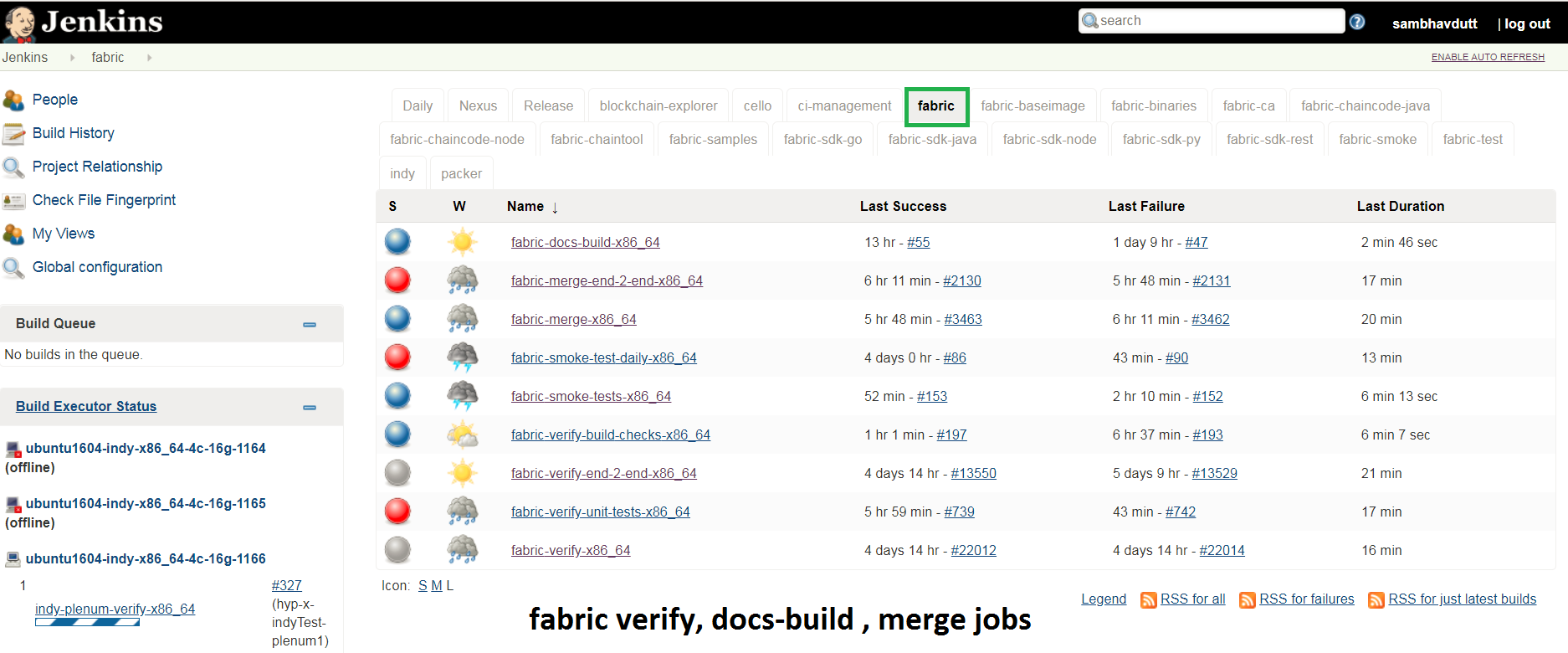
Views
Merge process for Fabric¶
Once the patchset is approved by CI and the maintainers, they will merge the patchset which triggers below Merge jobs on the latest Fabric commit (doesn’t use the patchset’s parent commit).
fabric-merge-end-2-end-x86_64: https://jenkins.hyperledger.org/view/fabric/job/fabric-merge-end-2-end-x86_64/
Step1: Clones the fabric-ca repository:
- Clones the latest commit from the Fabric fabric-ca repository and then checksout to the Branch. If the patchset is triggered on fabric-ca release-1.1 branch, script will checkout to release-1.1 branch.
- After the fabric-ca repository is cloned in the above step, CI script executes to build docker images to kick off the e2e tests.
Step 2: Executes the e2e tests:
Below are the tests triggers in Fabric e2e job:
- e2e-cli - Runs fabric/examples/e2e_cli tests.
- Executes the network_setup.sh that spins up the network with docker-compose file from fabric/examples/e2e_cli folder.
- e2e-cli - Runs fabric/examples/e2e_cli tests.
- e2e-node - Runs the sdk-node e2e tests (Executes gulp test
command).
- Clones fabric-sdk-node repository and will checkout to Branch
- Spins up network using the docker-compose file from test/fixtures folder
- Install nodejs 8.9.4 version
- RUN
istanbul cover --report cobertura test/integration/e2e.js
- e2e-node - Runs the sdk-node e2e tests (Executes gulp test
command).
- e2e-java - Runs e2e java integration tests.
- If the patchset is on release-1.0 branch, we ignore java e2e tests for now.
- If not, run the java e2e tests by executing
source cirun.sh
- e2e-java - Runs e2e java integration tests.
fabric-merge-x86_64: https://jenkins.hyperledger.org/view/fabric/job/fabric-merge-x86_64
Step1: Pulls the third party docker images:
- Pulls the fabric baseimage version third party docker images(kafka, zookeeper, couchdb). The image name is appended with ‘hyperledger’ and tagged with the latest tag.
Step2: Executes Fabric tests using below two commands:
make lintermake unit-test
After the verify or merge tests are executed, It is time to archive the logs (artifacts). CI publishes the logs(artifacts) on Jenkins console.
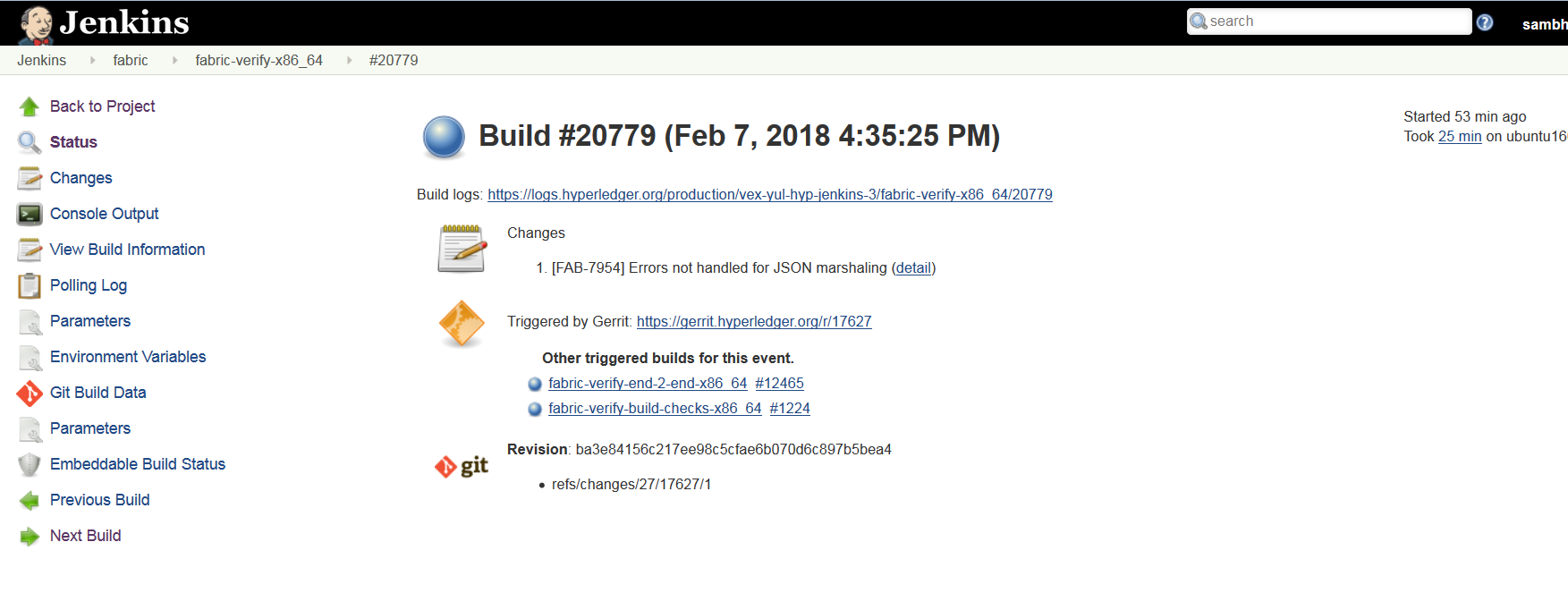
ConsoleOutPut
Build Notifications¶
The build results can be viewed on the Jenkins console, where depending on the result it displays with a colored bubble (green for success, red for failure).
Trigger failed jobs through Gerrit comments¶
Re-trigger of builds is possible in Jenkins by entering a comment to the Gerrit change that re-triggers a specific verify job. To do so, follow the below process:
Step 1: Open the Gerrit patchset for which you want to reverify the build
Step 2: Click on Reply, then type one of the below comments and click Post
VerifyBuild– Triggers fabric-verify-build-checks-x86_64 CI job, developers have to check the result of this job before posting the below comments on the patchset. As mentioned above, this job publishes images and binaries to nexus which further downloaded by SmokeTest and UnitTest jobs. Please make sure, images and binaries are published for that sepecific commit.
Run SmokeTest– Triggers fabric-smoke-tests-x86_64.
Run UnitTest– Triggers fabric-verify-unit-tests-x86_64.
Run DocsBuild– Triggers fabric-docs-build-x86_64
This kicks off the specified Fabric verify jobs. Once the build is triggered, verify the Jenkins console output and go through the log messages if you are interested to know how the build is making progress.
Questions¶
Please reach out to us in https://chat.hyperledger.org/channel/ci-pipeline or https://chat.hyperledger.org/channel/fabric-ci RC channels for any questions.